Question: What is the Structure of Courts in India?
Answer:
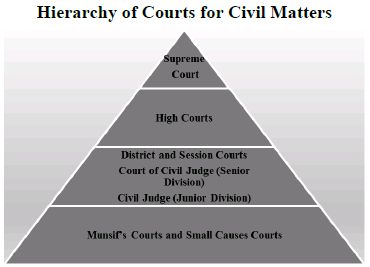
- There are three different levels of courts in our country.
- At district level, we have subordinate or district courts. At the state level, we have several High Courts. The High Court is the highest judicial authority in a state. At the top is the Supreme Court.
- The Supreme Court of India is the highest judicial authority. It is located in New Delhi and is presided over the Chief Justice of India. The decisions made by the Supreme Court are binding on all other courts in India.
- In India, we have an integrated judicial system, meaning that the decision made by higher courts are binding on the lower Courts.
Question: Why is there need for an independent judiciary? Discuss the hierarchy of courts.
Answer: Indian judiciary system is based on a three types hierarchy of court.
Need for an Independent Judiciary: The farmers of our Constitution have kept the Judiciary independent of the Legislature and the Executive so that
- It can check the misuse of powers by the other two organs of the government.
- Impartial justice is possible.
Question: Write a short note on Lok Adalat.
Answer: Lok Adalat: The process of seeking justice is time consuming and expensive in our country. For these reasons, Lok Adalat or the ‘People’s Court’ was set up to provide speedy justice. A Lok Adalat is presided over by a retired judge along with two other members, usually a lawyer and a social worker. The disputing parties put forward their own cases without advocates. The cases are solved through mutual understanding. No appeal can be made against the order of the Lok Adalat.
 Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students
Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students