Inside Our Earth: 7th Class NCERT CBSE SST – Geography
Question: How is the earth a dynamic planet?
Answer:
- The earth is our homeland
- It is a dynamic planet
- It is constantly undergoing changes inside and outside
Question: Have you ever wondered what lies in the interior of the earth? What is the earth made up of?
Answer: The interior has three major layers of rocks of different densities. The earth is made up of rocks.
Question: Describe the interior of the earth.
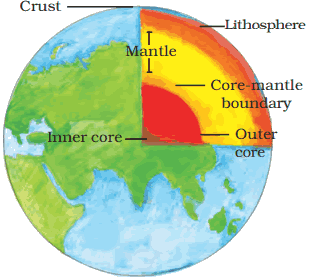
Answer: Interior of the Earth:
The earth is made up of several concentric layers with one inside another, just like an onion.
Crust:
- The uppermost layer on the earth’s surface is called the crust
- It is the thinnest of all the layers
- It is about 35 km, thick on the continental masses and only 5 km thick on the ocean floors
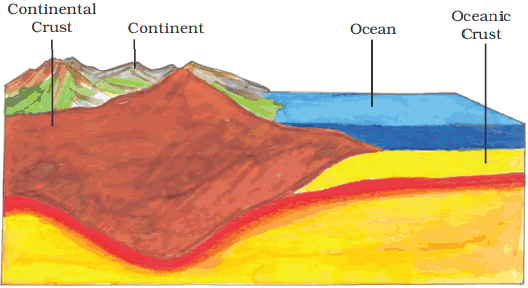
- Main minerals constituent of the continental mass are silica and alumina
- It is thus called sial (si – silica and al – alumina)
- The oceanic crust mainly consists of silica and magnesium.
- It is therefore called sima (si – silica and ma – magnesium).
Mantle
- Just beneath the crust is the mantle
- It extends up to a depth of 2900 km below the crust
Core
- The innermost layer is the core with a radius of about 3500 km
- It is mainly made up of nickel and iron
- Hence it is called nife (ni—nickel and fe—ferrous i.e., iron)
- The central core has very high temperature and pressure
Inside Our Earth: 7th Class SST – Question: What is earth’s crust made up of?
Answer: Earth’s crust is made up of different type of rocks. Rock is a natural mass of mineral matter. It is of different sizes, colors and texture and shapes. Earth is made up of sedimentary, igneous or metamorphic rocks.
Question: Describe igneous rocks.
Answer: Igneous Rocks
- The molten rock material is called magma
- When it cools, it becomes solid
- Rocks formed in this way are called igneous rocks
- They are also called primary rocks because other rocks are formed out of these rocks
There are two types of igneous rocks:
- Intrusive Rocks
- Extrusive Rocks
Formation of Extrusive and Intrusive Rocks:
- Due to extreme heat in the interior of the earth, rocks are found in the form of molten material called magma.
- When magma comes out on the surface of the earth, it cools down and turns into solid rocks. Such rocks are termed as extrusive rocks.
Examples:
- Basalt
- Deccan Trap is built of basalt
When the molten magma cools down within the interior of the earth, it becomes solid to form intrusive rocks.
Examples:
- Granite
- Garbo
Question: What is lava?
Answer: Lava is the hot red magma coming out from the interior of the earth to the surface. It cools down and become solid.
Question: What are two types of Igneous rocks?
Answer: Igneous rocks are formed by cooling of the lava. When the lava cools down on the crust it forms extrusive igneous rock for example basalt. They have grained structure.
Sometimes when it cools down deep inside the crust it forms intrusive igneous rocks. They have large grains for example Granite. Grinding stones are made of granite.
Question: Define the term sediment.
Answer: Rocks due to cracks and hitting, breakdown into smaller fragments called sediments.
Question: Give an account of sedimentary rocks.
Answer: Sedimentary Rocks
The small particles are called sediments
- These sediments are transported and deposited by wind, water etc. in low areas
- These loose sediments are compressed and hardened to form layers of rocks
- These layered rocks are called sedimentary rocks
Examples:
- Sandstone
- These rocks also contain fossils of plants, animals and other micro-organisms that once lived on them
Question: What are Fossils?
Answer: Fossils: The remains of dead plants and animals trapped in the layers of rocks are known as fossils.
Question: How are metamorphic rocks formed?
Answer: Igneous and Sedimentary rocks changes into metamorphic rocks under heat and pressure.
Metamorphic Rocks: When under heat and pressure igneous rocks and sedimentary rocks change their form and more precious rocks are formed to be known as metamorphic rocks.
Examples:
- Granite into granite gneiss
- Coal into slate
- Slate into schist
- Limestone into marble
Limestone is changed into marble due to the following reasons:
- The overlying layers of rocks put pressure on the underlying rocks
- From surface to interior of the earth, temperature and heat go on increasing
- Due to pressure and heat, the original limestone changes into marble
Question: What are the uses of rocks?
Answer: Uses of Rocks:
- Hard rocks are used in making buildings and barrages
- Houses and buildings are built of rocks (stones, slates, granite, marble)
- Stones are used in numerous games:
Seven stones (Phitthoo)
Hop scotch (Stapu, kit kit)
Five stones (Gitti) - Rocks (stones and slates) are used in building bridges, embankments.
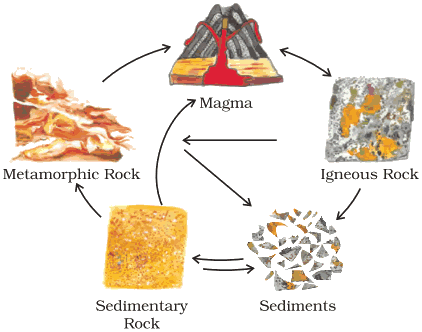
Question: Briefly describe the ‘rock cycle’.
Answer:
- One rock changes into another under certain conditions in a cyclic manner.
- Molten magma cools down and solidify to form igneous rocks. These rocks are broken down due to pressure and climatic conditions into sediments.
- These are transported and deposited to form sedimentary rocks. The igneous and sedimentary rocks under heat and pressure change into metamorphic rocks.
- These metamorphic rocks under great heat and pressure melt down to form molten magma. This again cools down to form igneous rocks. This process of transformation of rocks is called ‘rock cycle’.
Question: What are minerals? How are minerals important to us?
Answer: Minerals:
- Rocks are made up of different minerals
- Minerals are naturally occurring substances which have certain physical properties and definite chemical composition
- Minerals are very important to us
- Some are used as fuels
Examples:
- Coal
- Natural gas
- Petroleum
They are also used in industries as energy and raw material.
Examples:
- Iron
- Aluminium
- Gold
- Uranium
They are used in medicine, in fertilizers etc.
Question: Fill in the blanks with appropriate words:
- Lava is the molten magma from ……………………… of the earth’s surface.
- Like a ………………………, the earth is made up of ……………………… layers.
- Crust is about ……………………… km on the continental mass and ……………………… km on the ocean floor.
- Mantle forms about ……………………… of the earth’s volume.
- Core has a radius of about ……………………… km and has very high temperature and ………………………
- Limestone under excessive heat and pressure changes into ………………………
Answer:
- interior
- onion, concentric
- 35 and 5
- 16%
- 3500, pressure
- marble
Question: State whether the given statements are true or false:
- Crust is the thickest of all the layers
- Core is the innermost layer of the earth
- Mantle extends up to the depth of 2900 km
- The loose sediments are hardened to form metamorphic rocks
- Deccan plateau is made up of basalt
- Fossils are remains of dead plants and animals
Answer:
- False
- True
- True
- False
- True
- True
Question: Answer the following questions briefly.
- What are the three layers of the earth?
- What is a rock?
- Name three types of rocks.
- How are extrusive and intrusive rocks formed?
- What do you mean by a rock cycle?
- What are the uses of rocks?
- What are metamorphic rocks?
Answer:
- The three layers of the earth are:
Crust
Mantle
Core - A rock is a natural mass of mineral matter that makes up the earth’s crust. Rocks can be of different colour, size and texture.
- Three types of rocks are:
Igneous rocks also known as primary rocks
Sedimentary rocks
Metamorphic rocks - When the molten lava comes on the earth’s surface, it rapidly cools down and becomes solid. Rocks formed in this way on the crust are extrusive igneous rocks.
Sometimes the molten magma cools down deep inside the earth’s crust. Solid rocks so formed are actually intrusive igneous rocks. - One type of rock changes to another type under certain conditions in a cyclic manner. This process of transformation of the rock from one to another is known as the rock cycle. Let’s understand it through example—Igneous rocks change into sedimentary rocks. When the igneous and sedimentary rocks are subjected to heat and pressure, they change into metamorphic rocks. The metamorphic rocks which are still under great heat and pressure meet down to form molten magma. This molten magma again can cool down and solidify into igneous rocks.
- Hard rocks are used for making roads, houses and buildings. Stones are used in many games, such as seven stones (pitthoo), hopscotch (stapu / kitkit), Five stones (gitti).
- When the igneous and sedimentary rocks are subjected to heat and pressure they change into metamorphic rocks. For example, clay changes into slate and limestone into marble.
Question: Tick the correct answer:
- The rock which is made up of molten magma is
(a) Igneous (b) Sedimentary (c) Metamorphic - The innermost layer of the earth is
(a) Crust (b) Core (c) Mantle - Gold, petroleum and coal are example of
(a) Rocks (b) Minerals (c) Fossils - Rocks which contain fossils are
(a) Sedimentary rocks (b) Metamorphic rocks (c) Igneous rocks - The thinnest layer of the earth is
(a) Crust (b) Mantle (c) Core
Answer: (i) – (a), (ii) – (b), (iii) – (b), (iv) – (a), (v) – (a)
Question: Give reasons:
- We cannot go to the center of the earth
- Sedimentary rocks are formed from sediments
- Limestone is changed into marble
Answer:
- To reach the center of the earth one will have to dig a hole 6000 km. deep on the ocean floor. This is quite impossible and therefore we cannot go to the center of the earth.
- Rocks break down into small fragments known as sediments. These sediments are transported and deposited by wind, water, etc. These loose sediments are compressed and hardened to form layers of rocks known as sedimentary rocks.
- Limestone is changed into marble because igneous and sedimentary rocks change into metamorphic rocks under a great heat and pressure.
Question: What is called the uppermost layer of the earth?
Answer: It is called the crust.
Question: What is the special feature of this layer?
Answer. It is the thinnest of all the layers
Question: Name the main mineral constituent of the continental mass.
Answer: Silica and alumina
Question: Name the constituents of the oceanic crust.
Answer: Silica and magnesium.
Question: What is the radius of the core?
Answer: The radius of the core is about 3500 km.
Question: What are the main constituents of the core?
Answer: The main constituents of the core are nickel and iron. It is usually known as nife.
Question: What is the earth’s crust made of?
Answer: It is made up of different types of rocks.
Question: What are called igneous rocks?
Answer: When the molten magma cools, it becomes solid. Rocks formed in this way are called igneous rocks.
Question: What are fossils?
Answer: The remains of the dead plant and animals trapped in the layers of rocks are called fossils.
Question: What happens when igneous and sedimentary rocks go under great heat and pressure?
Answer: They change into metamorphic rocks.
Question: What are minerals? How are they useful for mankind?
Answer: Minerals are naturally occurring substances which have certain physical properties and definite chemical composition.
Minerals are very useful for mankind. Some minerals like coal, natural gas and petroleum are used as fuels. They are also used in industries. Iron, aluminium, gold, uranium etc. are used in medicine, in Fertilizers etc.
Inside Our Earth: 7th Class SST – Question: Mention various types of rocks:
Answer: Rocks are of the three types:
- Igneous rocks:
(i) Sedimentary rocks
(ii) Metamorphic rocks
(iii) Igneous rocksWhen the molten magma cools, it becomes solid. Rocks formed in this way are called igneous rocks. They are also called primary rocks. They are of two types—intrusive rocks and extrusive rocks. - Extrusive rocks: When molten lava comes on the earth’s surface, it rapidly cools down and becomes solid. Rocks formed in this way on the crust Eire called extrusive igneous rocks. For example: basalt.
- Intrusive rocks: Sometimes the molten magma cools down deep inside the earth’s crust. Solid rocks so formed are called intrusive igneous rocks. Since they cool down slowly they form large grains. For example, granite.
- Sedimentary rocks: Small fragments of rocks are called sediments. These sediments are transported and deposited by wind, water, etc.These loose sediments are compressed and hardened to form sedimentary rocks. For example, sandstone is made from grains of sand.
- Metamorphic rocks: When igneous and sedimentary rocks Eire subjected to great heat and pressure they change into metamorphic rocks. For example, clay changes into slate and limestone into marble.
Question: What do you know about the interior of the earth?
Answer: Our earth is made up of several concentric layers with one inside another. These layers are three in number – crust, mantle and core.
Crust: It is the uppermost layer over the earth’s surface. It is the thinnest of all the layers. It is about 35 km on the continental masses and only 5 km on the ocean floors.
The continental masses are made up of silica and alumina. It is thus called sial (si-silica and al-alumina). The oceanic crust mainly consists of silica and magnesium. It is thus called sima (si-silica and ma-magnesium).
 Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students
Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students